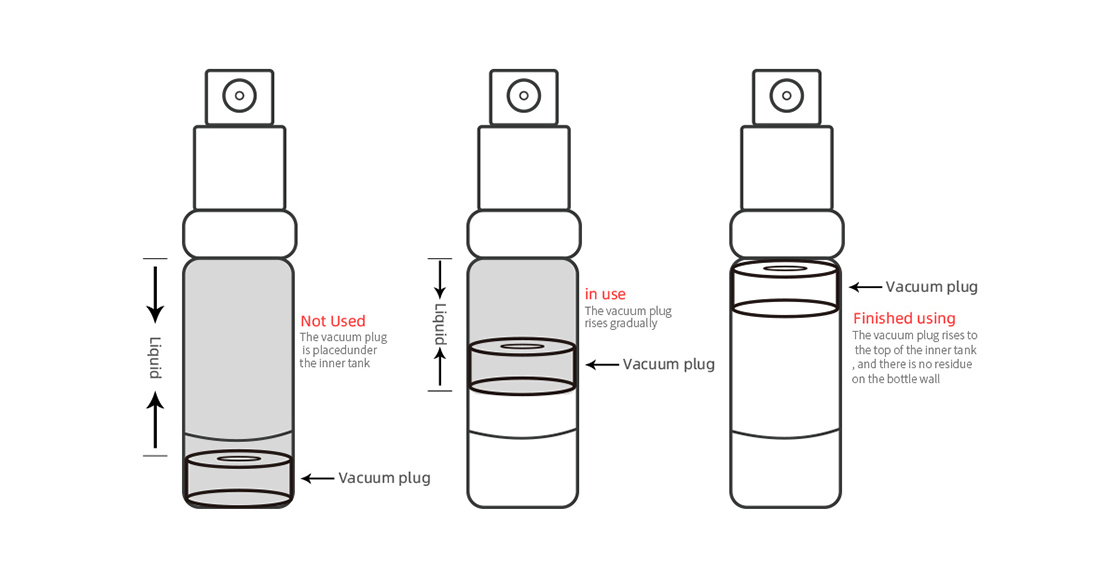
An airless bottle is a type of packaging that is designed to dispense products while minimizing air exposure. The mechanism behind an airless bottle involves a vacuum system that helps push the product up from the bottom of the bottle. Here’s a general explanation of how airless bottles work:
Construction: An airless bottle typically consists of three main components: the container, the piston, and the pump mechanism. The container holds the product, while the piston acts as a barrier between the product and the pump. The pump mechanism includes a pump, a tube, and a nozzle.
Vacuum effect: When you first use an airless bottle, the piston is pushed all the way down, creating a vacuum inside the bottle. This vacuum effect helps prevent air from entering the container and oxidizing the product, which can degrade its quality.
Dispensing the product: When you press the pump mechanism, it activates the vacuum system. The pump creates pressure, which pushes the piston upward. As the piston moves up, it propels the product toward the nozzle, allowing it to be dispensed. The airless design ensures that the product is continuously pushed up, minimizing wastage and ensuring efficient use.
No air exposure: One of the main advantages of airless bottles is that they minimize air exposure to the product. Traditional bottles with a dip tube can introduce air into the container as the product is used, causing oxidation and potentially reducing the product’s shelf life. With an airless bottle, the vacuum system ensures that the product is dispensed without allowing air to come into contact with it.

To use an airless bottle effectively, follow these steps:
1.Remove the cap or lid from the bottle.
2.Press the pump mechanism a few times to activate the vacuum system and prime the pump.
3.The product should start to dispense from the nozzle. Press the pump as needed to obtain the desired amount of product.
4.After use, replace the cap or lid securely to protect the remaining product from air exposure.
Airless bottles are commonly used for skincare products, such as serums, voiteet, and lotions, as well as other liquid or semi-liquid products that benefit from reduced air exposure.